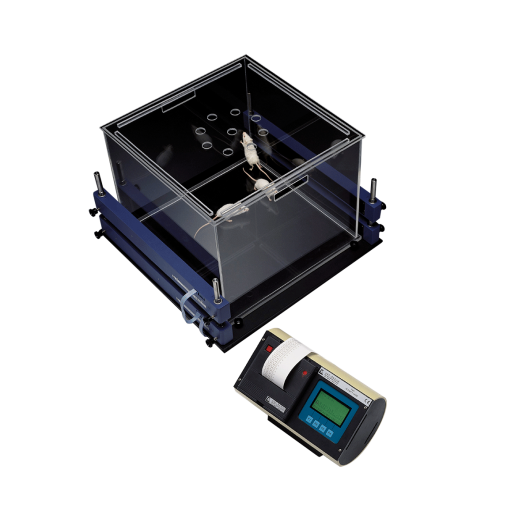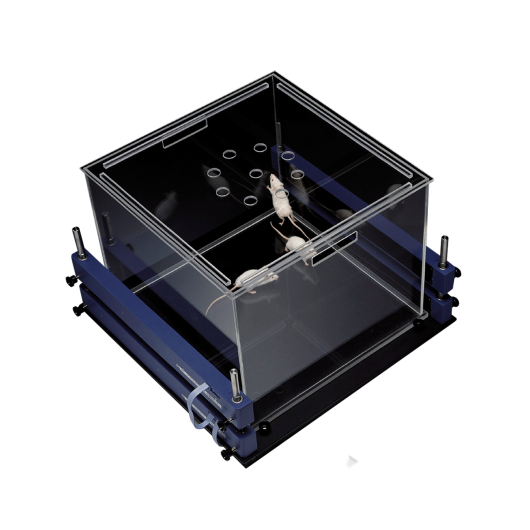
Activity Cage for recording of spontaneous coordinate activity in rats and mice
Features
- High-contrast colors
- Non-reflecting surface
- Ample color selection
- Reasonably rough “warm” surface texture
- Quality materials
Benefits
- Gives optimal results with any Video-Tracking software
- Guarantees optimal camera view and no glare
- Available in grey (standard), blue, white, black, custom color
- Selected for best rodent comfort, non-slippery
- Reliable and durable mazes, easy to clean and store
Application
Carol Barnes developed a maze test for spatial learning and memory in 1979 where animals escaped from a brightly lit, exposed circular open platform surface to a small dark recessed chamber located under one of the holes around the perimeter of the platform. Although it was initially invented for rats, the Barnes maze has become more popular to assess spatial memory in mice, taking advantage of their superior abilities to find and escape through small holes.
Visual cues are required to optimize cognitive performance: better performance are evidenced in mice tested with intra- and extra-maze cues than mice trained with no spatial cues present.
The Barnes Maze has similarities to the Morris Water Maze: both tasks measure the ability of a mouse to learn and remember the location of a target zone using a configuration of distal visual cues located around the testing area. Both tasks rely on hippocampal-dependent spatial reference memory and on the inherent tendencies of the subjects to escape from an aversive environment.
However, in the Barnes Maze no strong aversive stimuli is being used as reinforcement, which are likely to produce stress in the animal, influencing the performance in the task. It has been suggested that the Barnes maze is less anxiogenic.
Mostly reference memory and working memory has been studied using the Barnes Maze with different protocols, but more recently the Barnes Maze has been used in protocols to study short-term and long-term reference memory.
Method paper
- C. Barnes et alia: “Memory Deficits Associated with Senescence: a Neurophysiological and Behavioral Study in the Rat" J Comp Physiol Psychol.93(1):74-104, 1979
- B. Sunyer et alia: “Barnes Maze, a Useful Task to Assess Spatial Reference Memory in the Mice” Protocol Exchange: doi:10.1038/nprot.2007.390, 2007